Investors who hold many stocks in their hands encounter such a problem often. Although they keep bullish on the stocks in the long term, they are worried about the risk of the stocks in the short term. In this case, how to hedge the risk and reduce the loss caused by the stock’s decline is very important. While holding some stock positions, buying some put options of that stock is a good choice. Building a protective put option strategy can significantly reduce the loss caused by the stock decline, especially in a stock market crash. This article will teach you how to make a protective put option strategy step by step.
What is a put option?
A put option is a financial derivatives contract. The contract buyer has the right to sell certain shares to the put option seller at an agreed strike price before the expiration date. Put options allow investors to obtain income when the stock price goes down. If you own a stock and the stock price falls, you can use a put option to insure your stock position. Even if the stock price does not go down but goes up, the largest loss is only the option premium paid.
Related reading: What is an option? Everything you need to know. (basic knowledge for both call option and put option)
How to construct a protective put option strategy? (Step by Step)
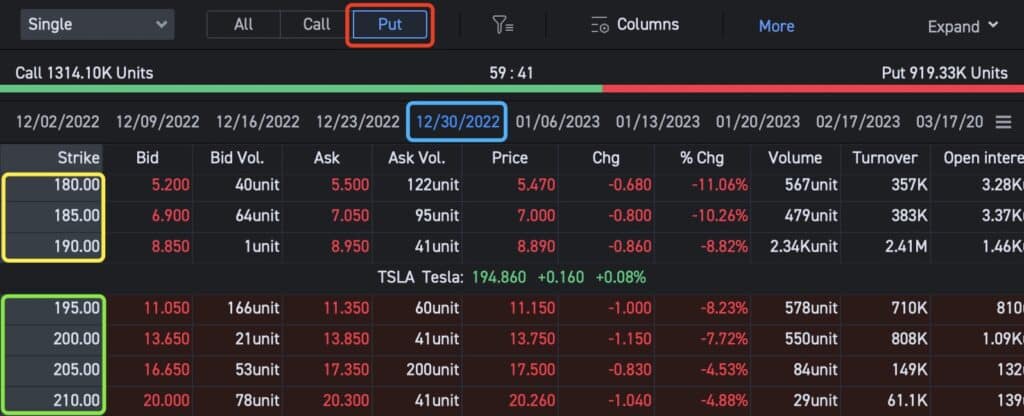
Open an option chain market interface, and select “put”. We can see that put options have different expiration dates and strike prices. How to choose the appropriate expiration date and strike price?
Pick the suitable expiration date
If you think the risk is temporary, you can buy a put option with a shorter tenor (the length of time remaining before the put option expires). Conversely, suppose you believe that stock prices are affected by macro factors (for example, the Fed’s quantitative tightening policy may last for a long time). In that case, there will be significant fluctuations for a long time in the future. Then it is more appropriate to buy a put option with a relatively long period (such as one year).
The prices of different put options are different. Generally speaking, the longer the option expiration time, the higher the option premium. That is equivalent to insurance with a more extended protection period for the stock.
Choose the right strike price
A strike price can be higher or lower than the current price. A put option with a strike price higher than the current price is called an in-the-money put option. A put option with a strike price lower than the current price is called an out-of-the-money put option. In-the-money options are more expensive than out-of-the-money options because in-the-money options have larger intrinsic value and a greater likelihood of being exercised.
Related Reading: Intrinsic Value And Time Value In Options.
When using a protective put option strategy, out of cost considerations, investors usually choose to buy out-of-the-money put options with lower prices.
How does the protective put option strategy affect profit and loss?
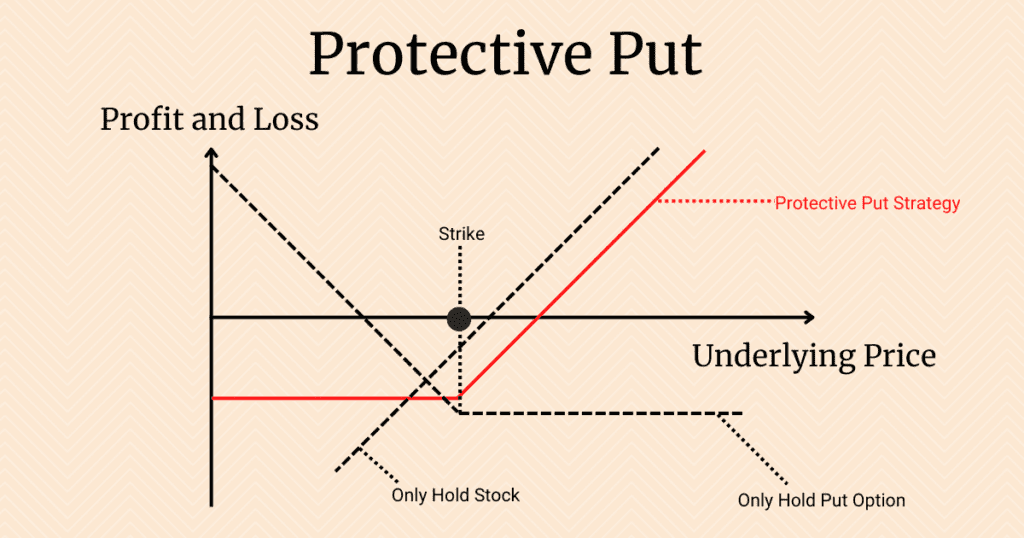
We can split the protective put option strategy into two situations: only holding stocks and only holding put options.
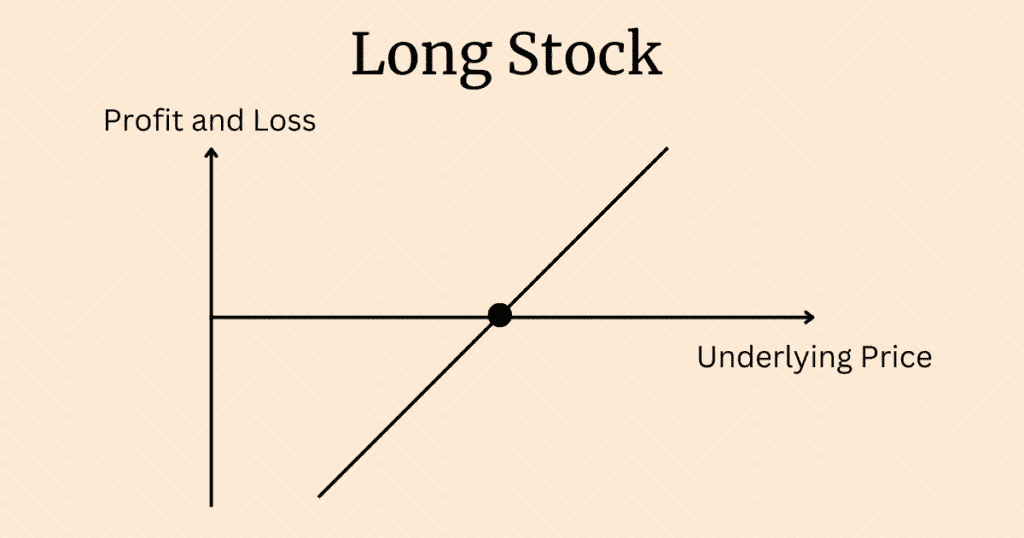
Only hold stocks situation
In this case, the investor’s total return grows linearly with the stock’s price.
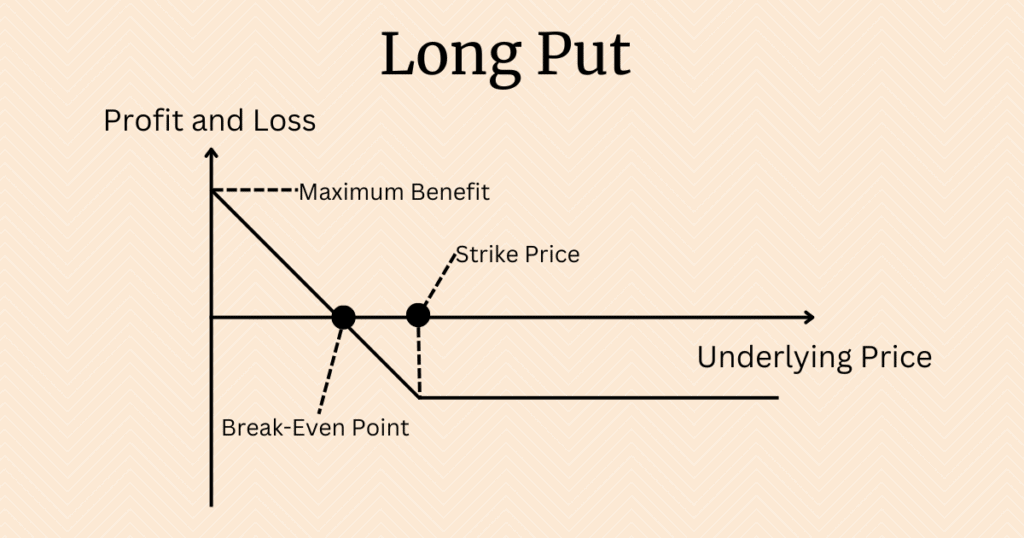
Only hold put options situation
The profit and loss chart for long put options is as follows:
Use the protective put option strategy (Case Study)
For this example, assume I own 100 shares of TSLA (Tesla Inc) stock (the cost is at $194.86) in the market and buy a put option (the cost is $5.47) with a strike price of $180 which will expire one month later.
When the option expires, if the stock price falls below $180, I can exercise the put option to sell the 100 shares of TSLA stock at $180. Then the total value of my portfolio is 17,453 (=(180-5.47)*100) dollars. Even if TSLA goes bankrupt and the stock price goes to $0, it has nothing to do with me because I have protected my position and locked in gains with a protective put option strategy.
I will not exercise the put option if the stock price does not fall below $180 when the option expires. Then the total value of my portfolio is the value of the TSLA stocks minus the premium. At this time, the portfolio’s value still increases linearly with the stock price of TSLA.
Conclusion
If you own stocks, buying a put option allows you to insure your stock position if the stock price goes down. There are a few things to keep in mind when buying put options.
- In-the-money options are more expensive than out-of-the-money options.
- The greater the implied volatility, the more expensive the premium.
- The longer the time until expiration, the more expensive the premium.
Of course, the protective put options strategy is not the only way to survive a stock market crash. There are many more ways you can hedge your risk with options. If you want to learn more about options trading strategies, you can visit Canny Trading.