What is a Growing Perpetuity?
A growing perpetuity represents a series of infinite cash flows that increase at a consistent rate over time.
In contrast to a simple perpetuity, which offers a steady and unchanging cash inflow, a growing perpetuity is dynamic. The cash flows originating from a growing perpetuity expand at a set growth rate, effectively safeguarding the real value of the cash flows against the erosive effects of inflation or other economic changes.
A practical application of growing perpetuities can be observed in the investment landscape. For example, consider an individual investing in stocks that not only pay dividends but also have a track record of incrementally increasing these dividends annually. In this scenario, the investor effectively engages with growing perpetuity. The dividends serve as the cash flows, and their annual increase corresponds to the growth rate intrinsic to a growing perpetuity.
Similarly, the real estate sector often showcases the characteristics of growing perpetuities through certain investment opportunities. Real estate properties that are rented out can produce a steady stream of rental income. If the rent is contractually designed to increase at a fixed rate annually, the investment can be perceived and analyzed as a growing perpetuity. This systematic increment in rent ensures that the property’s income-generating potential does not stagnate but instead keeps pace with, or possibly outstrips, economic changes and inflationary pressures.
Present Value of Growing Perpetuity Formula
The Present Value of Growing Perpetuity formula is computed by dividing the cash flow received in the first period by the difference between the discount rate and the growth rate. Within this formula:
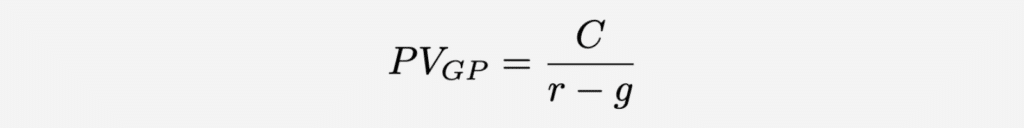
Where:
- PV is the Present Value;
- C is the initial cash flow;
- r is the discount rate;
- g is the growth rate.
Present Value of Growing Perpetuity Formula Derivation
The formula is derived from the concept of an infinite geometric series. In growing perpetuity, each future cash flow can be represented as C×(1+g)t, where t is the time period. Therefore, we can use this formula to discount the future cash flow back:
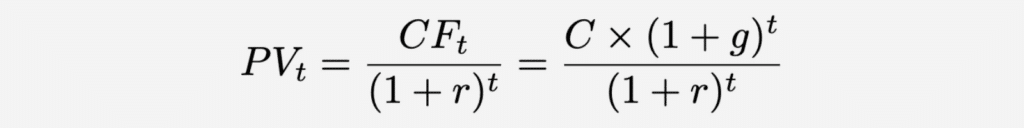
The present value of the entire series of cash flows is the sum of all PVt:
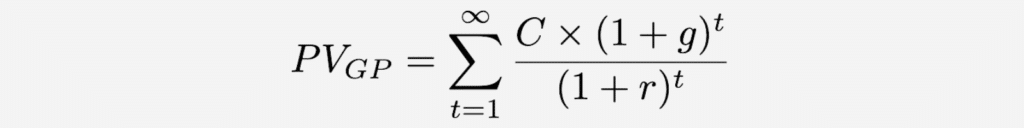
This is an infinite geometric series with a common ratio (1+g)/(1+r). The sum S of an infinite geometric series with first term a and common ratio b is given by:
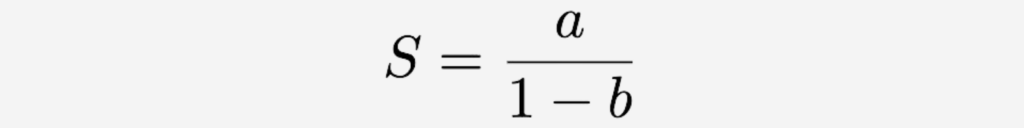
In our case, a=C/(1+r) and b=(1+g)/(1+r). Plugging these into the geometric series sum formula, we get:
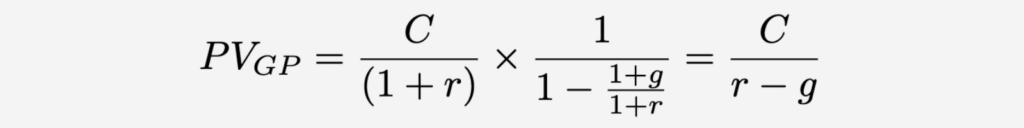
Present Value of Growing Perpetuity Calculation Example
Consider a tangible example: a real estate investment opportunity in the form of a rental property. At present, this property yields an annual rental income of $20,000. With a forecasted incremental increase of 3% per annum indefinitely, the rental income is expected to grow consistently. To evaluate the viability of this investment opportunity, it’s pivotal to calculate the Present Value (PV) grounded in the growing perpetuity model.
The Present Value of a Growing Perpetuity Formula is an invaluable tool to perform this calculation. To elucidate, let’s dissect the example further. If the rental income stands at $20,000 currently, and the anticipation is for this amount to experience a consistent 3% rise per annum, juxtapose this data against a discount rate set at 7%.
Using the formula, we calculate the Present Value (PV) as follows: $20,000 divided by the result of the discount rate (7%) subtracted by the perpetual growth rate (3%). This calculation results in a Present Value of $500,000.
What does this number signify for a potential investor? It sets a benchmark for the property’s value: if the property is listed at or below $500,000, it aligns with the investor’s required rate of return, taking into account the anticipated annual growth in rental income. Therefore, under these conditions, the property would be deemed a worthwhile investment.