In options trading, limit orders are invaluable tools enabling traders to manage risk effectively while optimizing returns. In this blog post, we’ll explore limit orders in options trading by addressing three fundamental questions: What is limit order in options trading? Why are they important to use? And how can they be executed on brokerage platforms?
What is a Limit Order in Options Trading?
A limit order allows traders to set a limit price for buying or selling an options contract. They execute only at the specified price or a more favorable one. This feature provides traders with better control over the execution price.
Due to the often volatile nature of the options market, many brokerages mandate setting a limit price for all options transactions. This requirement helps safeguard investors from unfavorable prices resulting from sudden market movements.
There are two primary types of limit orders in options trading:
Buy Limit Order: A buy limit order comes into play when a trader wishes to buy an options contract at a specific price or lower. It will execute only if the market price of the option falls to the determined limit price or below.
Sell Limit Order: A sell limit order is employed when a trader intends to sell an options contract at a specific price or higher. It will execute only if the market price of the option rises to the set limit price or above.
Why Should You Use Limit Orders in Options Trading?
Volatility and Leverage in Options
Options trading involves high leverage, which can lead to significant price fluctuations. These factors make it essential to set specific risk-reward parameters for your strategies. However, market orders cannot guarantee accurate execution prices, especially in a highly volatile options market, potentially causing profits and risks to deviate from your initial plan.
For instance, imagine you want to buy a call option with a limit price of $2.00, targeting the option to increase to $2.50, resulting in a 25% return. By using a limit order at $2.00, you can confidently expect a 25% return or better (if filled at a price below $2.00). However, if you use a market order amid substantial price fluctuations and get filled at $2.20, your potential returns are reduced to around 13.6%.
Liquidity and Bid-Ask Spread
Compared to stocks, options often have lower liquidity, leading to wider bid-ask spreads. Limit orders prevent you from paying excessive premiums caused by wide bid-ask spreads.
For example, an option may have a bid price of $3.00 and an ask price of $3.50. If you use a market order to buy the option, you might end up paying the full ask price of $3.50. However, by placing a limit order at $3.20, you can potentially save $0.30 per contract, significantly impacting your overall profitability.
Multi-Legged Options Strategies
Options strategies frequently involve multiple legs, which require precise execution prices for the overall strategy to succeed. If even one leg of the strategy executes at an unfavorable price due to a market order, the entire strategy could become ineffective or result in considerable losses.
Take the Jade Lizard strategy, for example, which consists of selling a put option and selling a call spread (selling a lower strike call and buying a higher strike call). The net credit received from these three transactions must exceed the width of the call spread. Otherwise, the strategy’s profit potential turns into a loss when the underlying price moves significantly higher. By using limit orders for each leg, you can ensure that the execution prices align with your strategy requirements, minimizing the risk of unanticipated losses.
Related Reading: Jade Lizard Options Strategy: Profit & Loss, Examples, Best Stocks
How to Place Limit Orders for Options?
In this concluding section, we will discuss how to place limit orders for options on brokerage platforms. While there may be minor variations between platforms, the process is typically quite similar for most. To provide a clear example, we will use Firstrade as our reference.
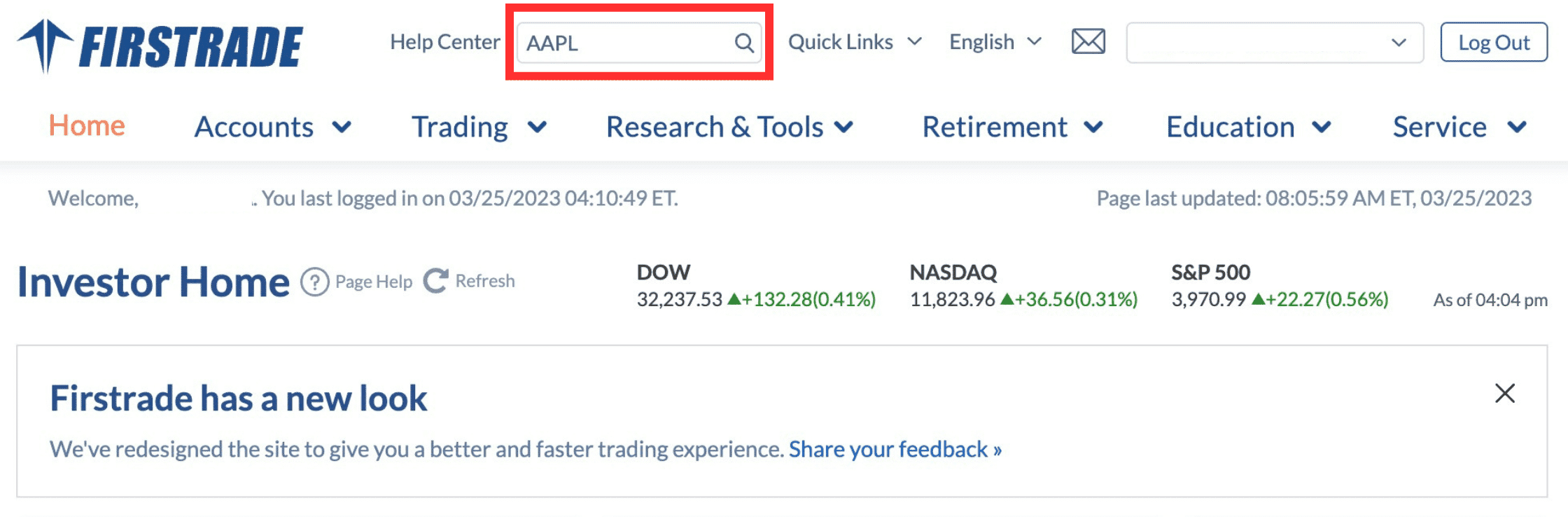
Search for the underlying asset: In the platform’s search box, enter the stock symbol of the underlying asset for which you want to trade options. For example, if you want to trade options for Apple Inc., you would enter “AAPL.”
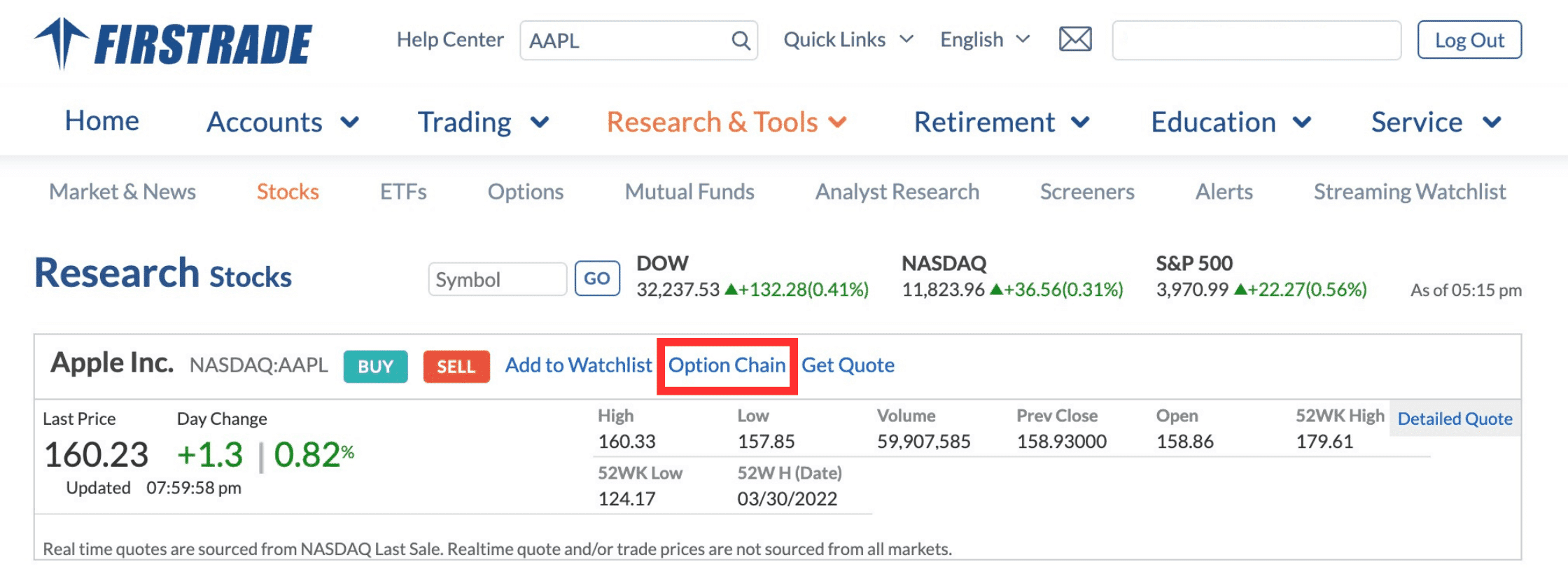
Select the options chain: When the information for the underlying asset is displayed on your screen, click on “Option Chain” (Desktop) or “Trade Options” (Mobile) to view the available options contracts.
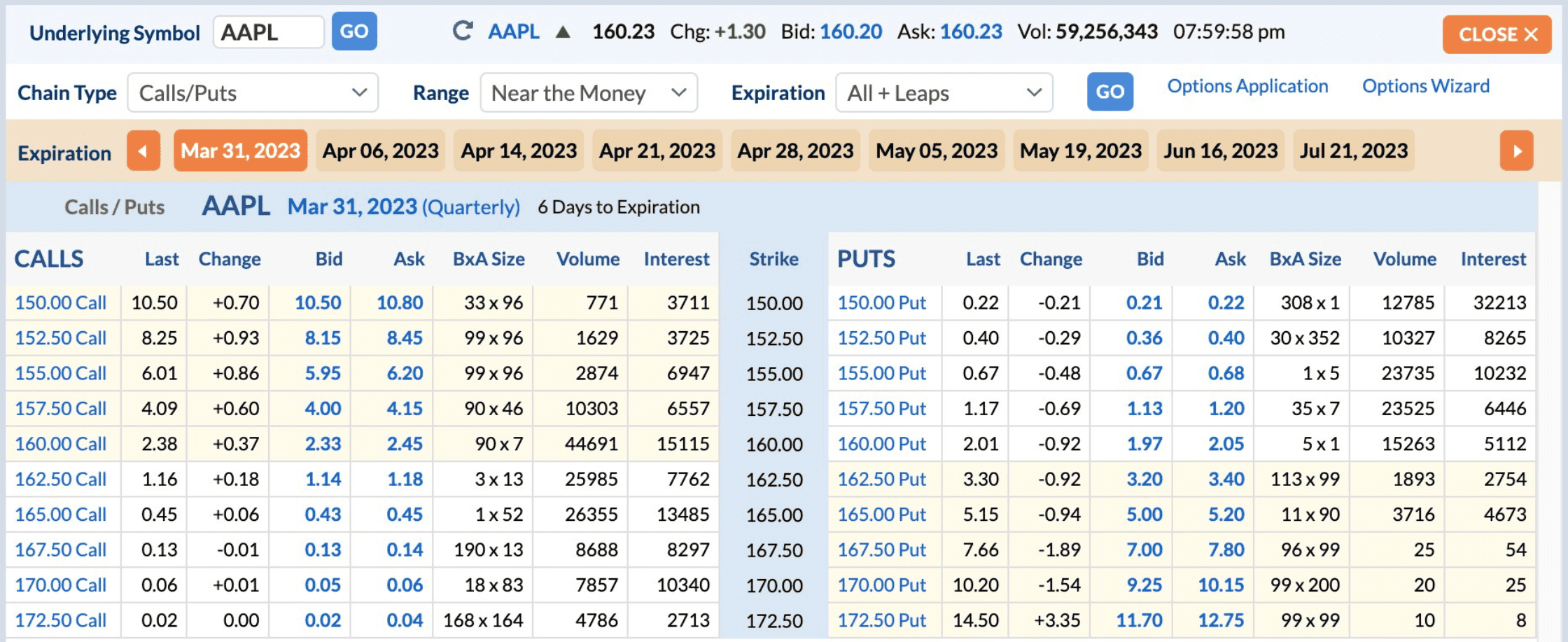
Choose the options contract: Within the options chain, locate the options contract you want to buy or sell. Pay attention to the expiration date, strike price, and whether it is a call or put option.
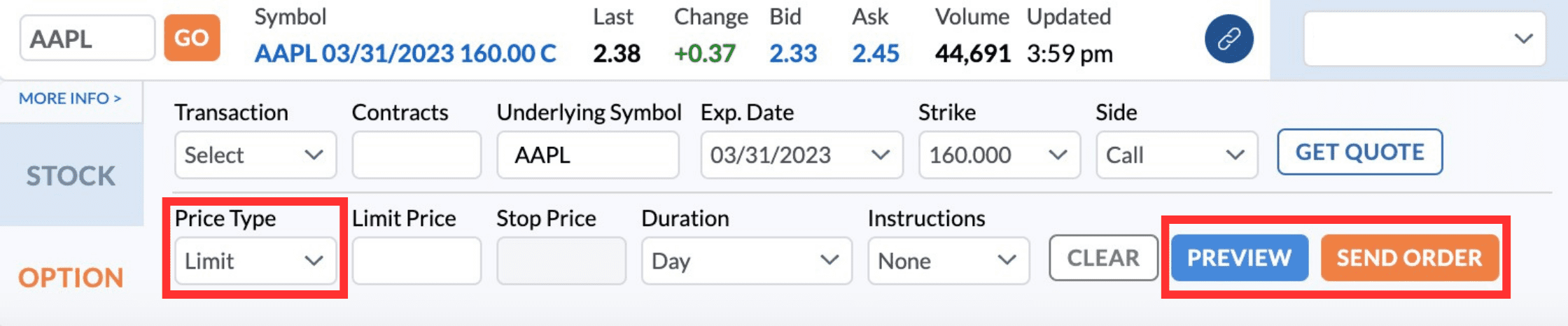
Set up the limit order: Click on your chosen options contract and select “Limit” as the price type in the window that pops up. Next, enter the maximum (for buying) or minimum (for selling) price at which you want to trade in the “Limit Price” field.
Set other parameters: You can also set additional parameters such as duration (Day or GT90 – Good for 90 Days), contracts (the number of options contracts you want to buy or sell), and other advanced settings. Please note that options trading is unavailable during extended hours.
Preview and submit: Once you confirm the information is accurate, click “Preview” for a final review. If everything looks good, click “Send Order” to send your limit order to the market.
By following these steps, you should be able to successfully place limit orders for options on Firstrade and other similar brokerage platforms. Ensure that you familiarize yourself with the features and functionalities of the platform you are using before actually trading.